Configuring your Cluster to Use Cadence Archival
Creating Cadence Clusters with Cadence Archival on AWS
Cadence Archival is a tiered storage feature of Cadence which enables workflow histories and visibility records to be stored in AWS S3 buckets following a retention period in your primary datastore cluster. More information about the usefulness and capabilities of this feature can be found in the official Cadence documentation, here: https://cadenceworkflow.io/docs/concepts/archival/ . This documentation will guide you through the process of enabling Cadence Archival on your Instaclustr managed Cadence cluster.
Please note that as a consequence of enabling archival, your cluster’s workflow histories and/or visibility records will be retained indefinitely in an S3 bucket within your AWS account. For this reason, before proceeding, we highly recommend implementing the following best practices to minimise risk to your business’s data:
- In keeping with the official advice from the Cadence project, workflows should never operate on plaintext sensitive data or personally identifiable information (PII). Please ensure that your workflows do not operate on unencrypted sensitive data or PII.
- Do not use your created S3 bucket for non-Archival purposes (i.e. storing Cadence-unrelated data).
- We recommend enabling access logging on your Archival S3 bucket. Directions for doing so can be found here: https://docs.aws.amazon.com/AmazonS3/latest/userguide/ServerLogs.html .
- We recommend enabling Object versioning on your Archival S3 bucket. This will either be done by default if creating a bucket using our CloudFormation template for Cadence clusters in Instaclustr’s account, or should be configured by you during bucket creation for Cadence clusters in your own AWS account.
Storage pre-setup for Cadence Clusters in Instaclustr’s account.
In this section we will be walking through utilizing an AWS CloudFormation template to provision a stack containing the required S3 bucket, Access Policy, User and User Access Keys to leverage Cadence Archival on your cluster. Note that this section of the guide is for Cadence clusters run in Instaclustr’s AWS account; see the section below if running in your own account.
- Create a CloudFormation template file instaclustr_cadence_archival_aws with the below content.
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108 109 110 111 112 113 114 115 116 117 118 119 120 121 122 123 124 125 126 127 128 129 130 131 132 133 134 135 136 137 138 139 140 141 142 143 144 145 146 147 148 149 150 151 152 153 154 155 156 157 158 159 160 161 162 163 164 165 166 167 168 169 170 171 172 173 174 175 176 177 178 179 180 181 182 183 184 185 186 187 188 189 190 191 192 193 194 195 196 197 198 199 200 201 202 203 204 205 206 207 208 209 210 211 212 213 214 215 216 |
{ "AWSTemplateFormatVersion": "2010-09-09", "Metadata": { "AWS::CloudFormation::Designer": { "640c4a44-ac96-4b5d-b51a-3ec830b9a0d2": { "size": { "width": 60, "height": 60 }, "position": { "x": 60, "y": 90 }, "z": 1, "embeds": [] }, "22a0401a-766a-463f-ab7f-f620425fb671": { "size": { "width": 60, "height": 60 }, "position": { "x": 60, "y": 190 }, "z": 1, "embeds": [], "dependson": [ "640c4a44-ac96-4b5d-b51a-3ec830b9a0d2" ] }, "3d6c0caa-7928-47aa-af65-a46ab2fd91c0": { "size": { "width": 60, "height": 60 }, "position": { "x": -30, "y": 280 }, "z": 1, "embeds": [] }, "22035e3c-4fbb-4a3d-a4e3-f5d48632651f": { "size": { "width": 60, "height": 60 }, "position": { "x": 140, "y": 280 }, "z": 1, "embeds": [], "dependson": [ "22a0401a-766a-463f-ab7f-f620425fb671" ] } } }, "Parameters": { "ResourceNamePrefixParameter": { "Type": "String", "Default": "instaclustr-cadence-archival-storage", "AllowedPattern": "[a-z0-9\\-]+", "Description": "AWS storage resources name prefix" } }, "Outputs": { "AccessKey": { "Value": { "Ref": "InstaclustrCadenceArchivalUserKey" }, "Description": "AWSAccessKeyId of new user" }, "SecretKey": { "Value": { "Fn::GetAtt": [ "InstaclustrCadenceArchivalUserKey", "SecretAccessKey" ] }, "Description": "AWSSecretKey of new user" }, "S3BucketName": { "Value": { "Ref": "InstaclustrCadenceArchivalBucket" }, "Description": "Name of S3 bucket to hold connector content" } }, "Resources": { "InstaclustrCadenceArchivalBucket": { "Type": "AWS::S3::Bucket", "Properties": { "BucketName": { "Fn::Join": [ "", [ { "Ref": "ResourceNamePrefixParameter" }, "-bucket" ] ] }, "VersioningConfiguration": { "Status": "Enabled" } }, "Metadata": { "AWS::CloudFormation::Designer": { "id": "640c4a44-ac96-4b5d-b51a-3ec830b9a0d2" } } }, "InstaclustrCadenceArchivalUser": { "Type": "AWS::IAM::User", "Properties": { "UserName": { "Fn::Join": [ "", [ { "Ref": "ResourceNamePrefixParameter" }, "-user" ] ] } }, "Metadata": { "AWS::CloudFormation::Designer": { "id": "22a0401a-766a-463f-ab7f-f620425fb671" } }, "DependsOn": [ "InstaclustrCadenceArchivalBucket" ] }, "InstaclustrCadenceArchivalUserKey": { "Type": "AWS::IAM::AccessKey", "Properties": { "UserName": { "Ref": "InstaclustrCadenceArchivalUser" }, "Status": "Active" }, "Metadata": { "AWS::CloudFormation::Designer": { "id": "3d6c0caa-7928-47aa-af65-a46ab2fd91c0" } }, "DependsOn": [ "InstaclustrCadenceArchivalUser" ] }, "InstaclustrCadenceArchivalUserAccessPolicy": { "Type": "AWS::IAM::Policy", "Properties": { "PolicyName": { "Fn::Join": [ "", [ { "Ref": "ResourceNamePrefixParameter" }, "-policy" ] ] }, "PolicyDocument": { "Statement": [ { "Effect": "Allow", "Action": [ "s3:ListBucket" ], "Resource": { "Fn::Join": [ "", [ "arn:aws:s3:::",{ "Ref": "ResourceNamePrefixParameter" }, "-bucket" ] ] } }, { "Effect": "Allow", "Action": [ "s3:PutObject" ], "Resource": { "Fn::Join": [ "", [ "arn:aws:s3:::",{ "Ref": "ResourceNamePrefixParameter" }, "-bucket/*" ] ] } }, { "Effect": "Allow", "Action": [ "s3:GetObject" ], "Resource": { "Fn::Join": [ "", [ "arn:aws:s3:::",{ "Ref": "ResourceNamePrefixParameter" }, "-bucket/*" ] ] } } ] }, "Users": [ { "Ref": "InstaclustrCadenceArchivalUser" } ] }, "Metadata": { "AWS::CloudFormation::Designer": { "id": "22035e3c-4fbb-4a3d-a4e3-f5d48632651f" } }, "DependsOn": [ "InstaclustrCadenceArchivalUser" ] } } } |
- Please log into your AWS console and access https://console.aws.amazon.com/cloudformation
- Click on the Create Stack dropdown and select With new resources option
- In the create stack view select Template is Ready for the Prerequisite – Prepare template section
- In the ‘Create Stack’ view select Upload a template file for the Specify template section
- Upload the previously created instaclustr_cadence_archival_aws CloudFormation template file and enter your choice of resource prefix that would be used for naming the resources created.
- Follow the rest of the create stack wizard according to the requirements of your account.
- Once the stack creation is complete you will be able to access the S3 bucket name, the created user access key, and the secret key required. This will be in the CloudFormation stack’s ‘Output’ view.
Storage pre-setup for Cadence Clusters in your own account.
In this documentation we will be walking through leveraging Cadence Archival on your cluster. Note that this section of the guide is for Cadence clusters run in your own AWS account; see the section above if running in Instaclustr’s account.
- Please log into your AWS console and access https://s3.console.aws.amazon.com/s3/buckets
- Follow the standard process to provision an S3 bucket as your archival storage in the AWS region of your choosing. Please enable Object versioning on your bucket at this stage. There are no other specific requirements in terms of permissions or access configuration that we require during the bucket configuration process.
- Make a note of the bucket name and region for your reference when provisioning your Cadence cluster.
Provisioning an Archival-enabled Cadence Cluster
- Navigate to the Instaclustr console at https://console2.instaclustr.com
- Follow our guide at https://www.instaclustr.com/support/documentation/cadence/getting-started-with-cadence/creating-a-cadence-cluster/ to get started provisioning a Cadence cluster. The specific steps that you will need to take in order to enable Cadence Archival on this cluster are the following:
- On the ‘Options’ page of the Cadence creation wizard, select ‘Enable Cadence Archival’
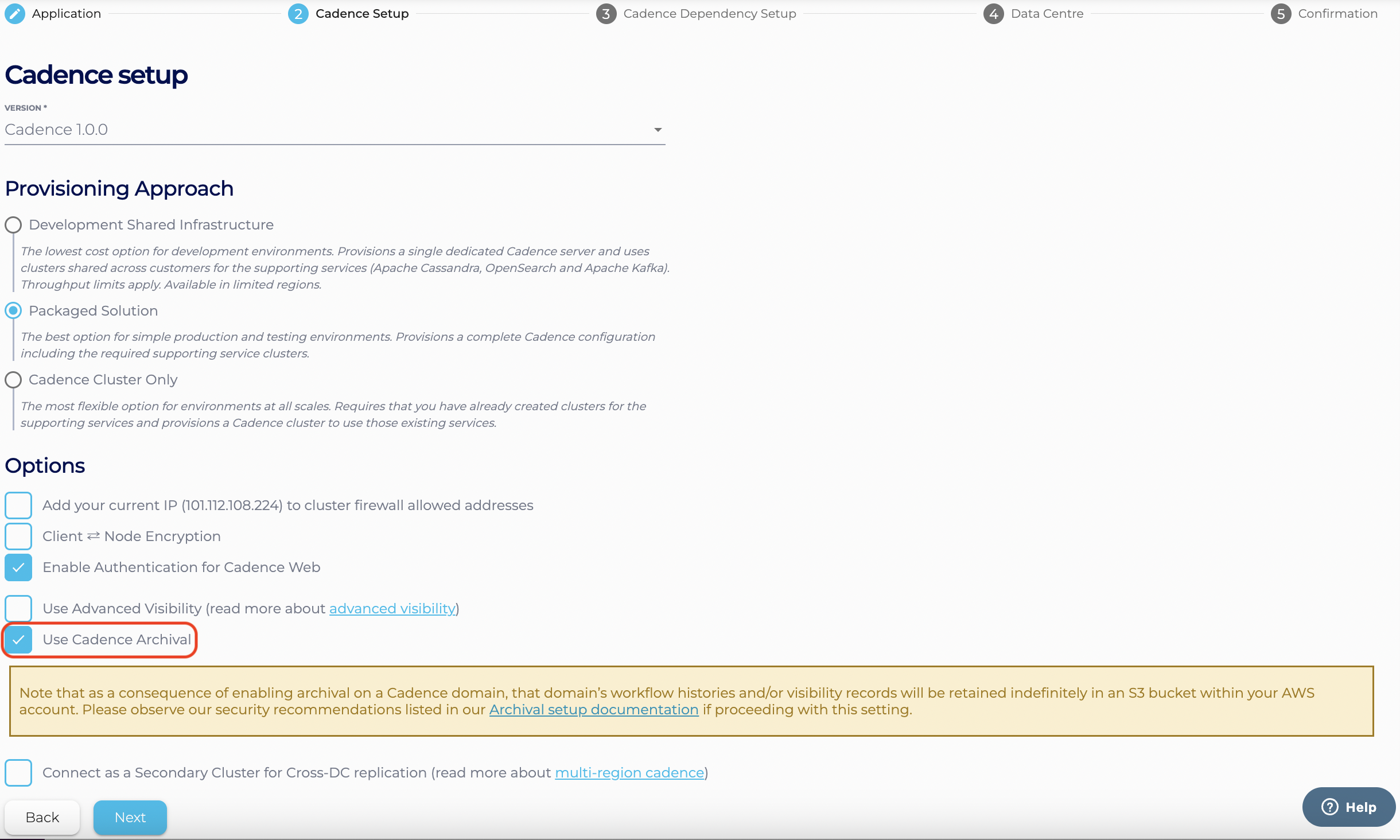
- On the ‘Data Centre’ page of the Cadence creation wizard, you will be asked to enter the following information to configure your archival setup.
- The URI that you wish to target for your archival. This is formed by the bucket file path prefixed by ‘s3://’. For example, if you have generated an S3 bucket called example-bucket, you might wish to target the URI s3://example-bucket. Or, if you have a directory in that bucket called ‘my-cluster’, you might target the URI s3://example-bucket/my-cluster. If running in Instaclustr’s account, the name of your bucket can be retrieved from the ‘Outputs’ tab of your CloudFormation stack view.
- The region that your S3 resource was created in, in lowercase and hyphen-separated e.g. us-east-1, us-west-2, etc.
- Clusters in Instaclustr’s account only: The AWS Access Key ID of the created stack’s IAM user (available in the stack ‘Outputs’ tab).
- Clusters in Instaclustr’s account only: The AWS Secret Access Key of the created stack’s IAM user (available in the stack ‘Outputs’ tab).

- On the ‘Options’ page of the Cadence creation wizard, select ‘Enable Cadence Archival’
Utilising Archival
Once your archival-enabled Cadence cluster is in a running state, simply create a domain with history and/or visibility archival enabled in order to begin leveraging this feature, like so.
|
1 |
cadence --ad <ADDRESS> --do sample-domain domain register --global_domain=false --retention <RETENTION_PERIOD> --vas enabled --has enabled |
 By Instaclustr Support
By Instaclustr Support


