What is OpenSearch?
OpenSearch is an open source search and analytics suite to derive insights from vast amounts of data. As a fork of Elasticsearch and Kibana, it offers many similar features with added transparency and community-driven input.
Initially developed by Amazon Web Services (AWS), OpenSearch has become a scalable search engine platform for diverse use cases including log analytics, full-text searches, and monitoring large volumes of data across various domains.
OpenSearch is compatible with the Elasticsearch API, making the transition easy for users familiar with Elasticsearch. OpenSearch supports real-time or near-real-time data processing and analytics. It also incorporates data visualization tools, security functionalities, and the ability to handle complex queries and aggregations.
How OpenSearch works
OpenSearch operates as a distributed system, leveraging a cluster-based architecture to handle large datasets. The core functionality revolves around its ability to index, search, and analyze data using a combination of nodes, indices, and shards:
- Cluster and nodes: An OpenSearch cluster is made up of one or more nodes, where each node is an instance of OpenSearch. Nodes collaborate to manage data and perform tasks like indexing and query execution. The cluster assigns roles to nodes, such as master nodes for managing cluster state and data nodes for storing and processing data.
- Indices and shards: Data in OpenSearch is organized into indices, which are logical collections of documents. Each index is divided into shards to enable parallel processing. Shards are distributed across nodes, ensuring scalability and fault tolerance. By using replicas—copies of primary shards—OpenSearch provides high availability and resilience.
- Indexing data: When data is ingested into OpenSearch, it is stored in a structured format using an inverted index, which optimizes search operations. OpenSearch supports multiple ingestion methods, such as APIs, log pipelines, and connectors to external sources like databases.
- Query execution: OpenSearch supports a query DSL (domain-specific language) for performing full-text searches, aggregations, and filtering. Queries are distributed across the cluster, and results are aggregated before being returned to the user. This parallelized approach ensures high performance, even for complex queries.
- Data visualization and monitoring: OpenSearch Dashboards provide tools for creating interactive visualizations and dashboards. These tools allow users to explore their data, identify patterns, and monitor system metrics in real time.
Security features: OpenSearch includes built-in security capabilities like user authentication, access control, and data encryption. These features are critical for protecting sensitive information and ensuring compliance with industry standards.
Tutorial 1: Installing OpenSearch using Helm
This tutorial provides a step-by-step guide for deploying OpenSearch in a Kubernetes cluster using Helm, a package manager for Kubernetes. Helm simplifies the deployment and management of OpenSearch by using predefined configurations and templates.
Prerequisites
Before you begin, ensure the following:
- A Kubernetes cluster is set up and running with at least 8 GiB of memory. A smaller allocation, such as 4 GiB, may result in deployment failure.
- Helm is already installed on your system. Refer to the Helm documentation for installation steps.
Step 1: Add the OpenSearch Helm repository
Start by adding the OpenSearch Helm repository to your Helm configuration:
|
1 |
helm repo add opensearch https://opensearch-project.github.io/helm-charts/ |

Update the list of available charts from all repositories:
|
1 |
helm repo update |

Step 2: Search for OpenSearch Helm charts
You can verify the availability of OpenSearch Helm charts by running:
|
1 |
helm search repo opensearch |

The command will return a list of available charts:
|
1 2 3 4 |
NAME CHART VERSION APP VERSION DESCRIPTION opensearch/opensearch 2.28.0 2.18.0 A Helm chart for OpenSearch opensearch/opensearch-dashboards 2.25.0 2.18.0 A Helm chart for OpenSearch Dashboards opensearch/data-prepper 0.1.0 2.8.0 A Helm chart for Data Prepper |
Step 3: Deploy OpenSearch
To deploy OpenSearch with the default configuration, execute the following command:
|
1 |
helm install example-deployment opensearch/opensearch |
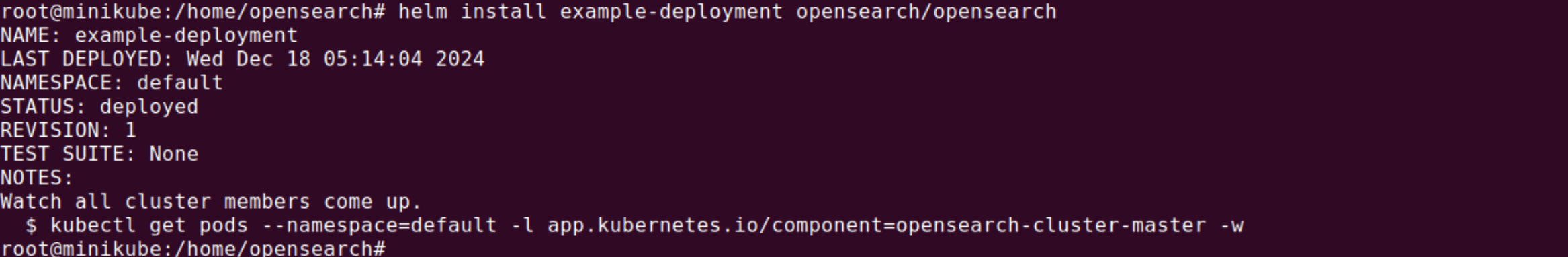
Step 4: Customize the deployment (optional)
For custom configurations, you can create a customvalues.yaml file with your desired settings. For example, to set a custom admin password for OpenSearch versions 2.12 or later, include the following in your values.yaml file:
|
1 2 3 |
extraEnvs: - name: OPENSEARCH_INITIAL_ADMIN_PASSWORD value: <my-admin-password> |
Deploy OpenSearch with the custom configurations:
|
1 |
helm install example-deployment --values=customvalues.yaml opensearch/opensearch |
Step 5: Verify the deployment
Check the status of the deployed pods:
|
1 |
kubectl get pods |
Sample output:
|
1 2 3 4 |
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE opensearch-cluster-master-0 1/1 Running 0 4m12s opensearch-cluster-master-1 1/1 Running 0 4m12s opensearch-cluster-master-2 1/1 Running 0 4m12s |

Step 6: Access the OpenSearch shell
To interact directly with the OpenSearch cluster, use the following command:
|
1 |
kubectl exec -it opensearch-cluster-master-0 -- /bin/bash |

Step 7: Test OpenSearch
Finally, test that OpenSearch is running by sending an API request to the cluster:
|
1 |
curl -XGET https://localhost:9200 -u 'admin:admin' --insecure |
Sample response:
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 |
{ "name" : "opensearch-cluster-master-1", "cluster_name" : "opensearch-cluster", "cluster_uuid" : "vP3gx6bPS2ELm7Y8qXm8ZW", "version" : { "distribution" : "opensearch", "number" : "3.2.1", "build_type" : "tar", "build_hash" : "xyz4321", "build_date" : "2024-12-02T00:00:00Z", "build_snapshot" : false, "lucene_version" : "9.1.0", "minimum_wire_compatibility_version" : "6.8.0", "minimum_index_compatibility_version" : "6.0.0-beta1" }, "tagline" : "The OpenSearch Project: https://opensearch.org/" |
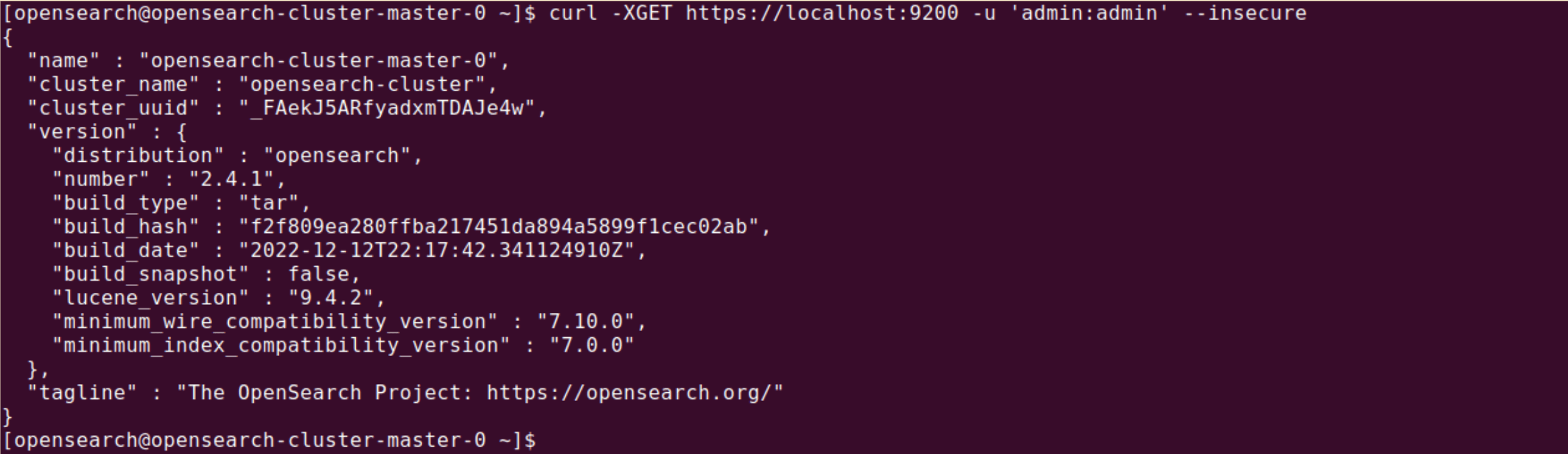
By following these steps, you should have a fully functioning OpenSearch deployment in your Kubernetes environment.
Tips from the expert
Kassian Wren
Open Source Technology Evangelist
Kassian Wren is an Open Source Technology Evangelist specializing in OpenSearch. They are known for their expertise in developing and promoting open-source technologies, and have contributed significantly to the OpenSearch community through talks, events, and educational content
In my experience, here are tips that can help you better utilize and optimize OpenSearch for search, analytics, and large-scale deployments:
- Fine-tune shard allocation for better performance: Avoid oversharding by carefully estimating the size of your data and choosing an optimal number of primary and replica shards. Oversharding leads to increased resource usage, while undersharding can limit performance. Use
_cat/shardsto monitor shard distribution. - Optimize the inverted index with proper mappings: By default, OpenSearch creates an inverted index for all fields, which can increase storage costs and slow down searches. Use explicit mappings to mark fields as
keyword,text, ordisabledto suit your queries and data retrieval needs. - Use ILM (Index Lifecycle Management) for data retention: Implement ILM policies to automate the management of indices based on their lifecycle (hot, warm, cold, or delete phases). This is crucial for log analytics where old data becomes less relevant and reduces the need for manual housekeeping.
- Leverage Painless scripting for advanced query logic: Use OpenSearch’s scripting capabilities (Painless) for custom scoring, data transformations, or filtering logic that cannot be achieved using standard queries. Be cautious about script execution overhead to avoid performance bottlenecks.
- Cache query results for repetitive searches: OpenSearch provides query caching for frequent, identical queries. Use
request_cacheand ensure you structure queries efficiently to take advantage of caching, especially in dashboards with repetitive aggregations.
Tutorial 2: Creating and searching for documents in Amazon OpenSearch Service
Set Up Amazon OpenSearch Service
To use Amazon OpenSearch Service APIs, the AWS CLI must be installed and configured. While not required for the web console, the CLI simplifies interaction with the service for scripting and automation.
- Install the AWS CLI: Follow the AWS CLI installation guide to set up the CLI on your system.
- Configure the AWS CLI: Use the
aws configurecommand to securely set your access keys, preferred AWS region, and output format:1aws configureExample configuration for a named profile:
12345[opensearch profile name]aws_access_key_id = IAM-USER-ACCESS-KEY-IDaws_secret_access_key = SECRET-IAM-USER-ACCESS-KEY-IDregion = us-west-1output = text - Verify the setup: Run a simple command to confirm:
1aws opensearch help
Add a document to the index
You can add documents using tools like cURL, Postman, or the OpenSearch Dashboards developer console.
- Access OpenSearch Dashboards: Navigate to your OpenSearch Dashboards URL (e.g.,
https:///_dashboards/) and log in. - Add a document: Use the
PUTcommand to create an index and add a document:12345PUT objects/_doc/3{"name": "car","color": "blue"} - Response:
123456789101112{"_index": "objects","_type": "_doc","_id": "3","_version": 1,"result": "created","_shards": {"total": 2,"successful": 2,"failed": 0}}
Create and automatically generated ID
OpenSearch can generate IDs for documents if not explicitly provided.
- Use
POSTto add a document:123456POST objects/_doc{"name": "table","color": "brown","classification": "furniture"} - Response:
1234567891011{"_index": "veggies","_type": "_doc","_id": "3WgyS4IB5DLqbRIvLxtF","result": "created","shards": {"total": 2,"successful": 2,"failed": 0}}

Update a document using the POST command
To update an existing document, use the document’s ID in a POST request.
- Create a document:
12345POST objects/_doc/38{"name": "orange","color": "orange"}
- Update the document:
123456POST objects/_doc/38{"name": "orange","color": "orange","classification": "fruit"}
- Response:
123456{"_index": "objects","_id": "38","result": "updated","_version": 2}

Perform bulk actions
The _bulk API allows multiple actions in a single request, reducing overhead.
Example bulk request:
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 |
POST /_bulk { "create": { "_index": "vegetables", "_id": "8" } } { "name": "artichoke", "color": "brown", "classification": "flower" } { "create": { "_index": "vegetables", "_id": "9" } } { "name": "onion", "color": "white", "classification": "bulb" } { "delete": { "_index": "vegetables", "_id": "1" } } |

Each action consists of two JSON lines: metadata and data.
Search for documents
OpenSearch supports basic and advanced search queries.
Basic search:
|
1 |
GET vegetables/_search?q=name:a* |
Searches for documents where the name field starts with “o”.

Advanced search:
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 |
GET vegetables/_search { "query": { "term": { "name": "onion" } } } |

Sorted search:
Recreate the index with sortable fields:
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 |
PUT vegetables { "mappings": { "properties": { "name": { "type": "keyword" }, "color": { "type": "keyword" }, "classification": { "type": "keyword" } } } } |

- Perform a sorted query:
1234567GET vegetables/_search{"query": {"term": { "color": "light-green" }},"sort": ["classification"]}

Instaclustr for OpenSearch: Unlocking the power of scalable search and analytics
Instaclustr for OpenSearch offers managed services that take the complexities of deploying and maintaining this robust platform off your plate. With expertise in open source technologies, Instaclustr ensures that your OpenSearch clusters are optimized, scalable, and always available, allowing you to focus on what truly matters: building great products and improving your customer experience.
Instaclustr for OpenSearch
When it comes to using OpenSearch, Instaclustr provides several key benefits:
- Fully managed OpenSearch
Get end-to-end management for your OpenSearch deployment, including setup, scaling, monitoring, and routine maintenance. We handle the grunt work so your team can stay focused on scaling your business. - High availability & scalability
Achieve high availability with multi-node configurations that provide failover capabilities. Whether you’re running a small application or scaling to enterprise-grade workloads, Instaclustr helps your OpenSearch clusters grow seamlessly with your business needs. - Open source expertise
Instaclustr champions open source technology, eliminating vendor lock-in and offering transparent pricing. This commitment ensures that your OpenSearch deployment is always community-driven, independently audited, and aligned with the latest developments in the ecosystem. - World-class support
Receive 24/7 support from seasoned engineers who specialize in OpenSearch. No chatbots; just real people ready to solve real problems and help you make the most of your investment. - Monitoring and optimization
Instaclustr doesn’t just manage your OpenSearch cluster—we actively monitor and optimize its performance. Advanced analytics and proactive alerts mean you’re always one step ahead when it comes to performance issues.
For more information see: