What Is OpenSearch?
OpenSearch is an open source search and analytics suite for applications that require fast, scalable search capabilities. It was developed as a fork of Elasticsearch 7.10.2 after Elastic changed its licensing model. OpenSearch is maintained under the Apache 2.0 license, ensuring it remains free and open for all users.
OpenSearch provides distributed search, log analytics, and observability functionality. It consists of two main components:
- OpenSearch: A search and analytics engine capable of handling structured and unstructured data.
- OpenSearch Dashboards: A visualization tool for exploring data, creating charts, and managing OpenSearch indices.
One of the primary ways to install OpenSearch is via the official Helm chart. We’ll show how to use the Helm chart to quickly deploy OpenSearch in a Kubernetes cluster.
What are Helm charts?
Helm charts are packages of pre-configured Kubernetes resources that simplify the deployment and management of applications on Kubernetes clusters. Helm, often referred to as the “package manager for Kubernetes,” uses charts to bundle YAML configuration files, templates, and metadata into reusable units.
A Helm chart contains all the Kubernetes manifests needed to deploy an application, including pods, services, deployments, and other resources. This modular packaging allows developers to:
- Automate deployments: Helm simplifies repetitive tasks like creating and managing Kubernetes objects.
- Customize configurations: Charts can accept user-defined values, enabling flexibility while maintaining standard templates.
- Version control: Helm charts are versioned, allowing easy rollback to previous configurations.
Helm charts simplify complex application setups, making it easier for teams to share, deploy, and maintain Kubernetes-based applications at scale. Popular applications like Prometheus, NGINX, and MySQL are commonly deployed using Helm charts.
Quick tutorial: Install OpenSearch using Helm and Helm charts
In this tutorial, you will learn how to install and configure OpenSearch using Helm, a package manager for Kubernetes. Helm simplifies the process of deploying OpenSearch by providing pre-configured resources in Helm charts.
Prerequisites
Before installing OpenSearch, ensure the following:
- Kubernetes cluster: You need access to a Kubernetes cluster.
- Memory requirements: At least 8 GiB of memory is recommended for a three-node cluster deployment.
Step 1: Helm install
Before deploying OpenSearch, ensure Helm is installed on your system. Helm is required to manage and deploy charts to a Kubernetes cluster.
- You can install Helm using a script or a package manager. For example, using the script provided by the Helm team:
1curl -fsSL -o get_helm.sh https://raw.githubusercontent.com/helm/helm/main/scripts/get-helm-3
 1chmod 700 get_helm.sh
1chmod 700 get_helm.sh 1./get_helm.sh
1./get_helm.sh - To confirm Helm is successfully installed, run:
1helm version

- You should see output similar to the following:
1version.BuildInfo{Version:"v3.x.x", GitCommit:"xxxxxxxxxx", GitTreeState:"clean", GoVersion:"go1.xx.x"}
Step 2: Add the OpenSearch Helm chart repository
With Helm installed and verified, you are ready to proceed with adding the OpenSearch Helm chart repository.
- First, add the official OpenSearch Helm chart repository to your local Helm configuration:
1helm repo add opensearch https://opensearch-project.github.io/helm-charts/

- Update the Helm chart repositories to fetch the latest available charts:
1helm repo update

- Verify the OpenSearch charts by searching the repository:
1helm search repo opensearch

The output should display OpenSearch and OpenSearch Dashboards charts:1234NAME CHART VERSION APP VERSION DESCRIPTIONopensearch/opensearch 2.0.5 2.0.0 A Helm chart for OpenSearchopensearch/opensearch-dashboards 2.0.3 2.0.0 A Helm chart for OpenSearch Dashboards
Step 3: Deploy OpenSearch
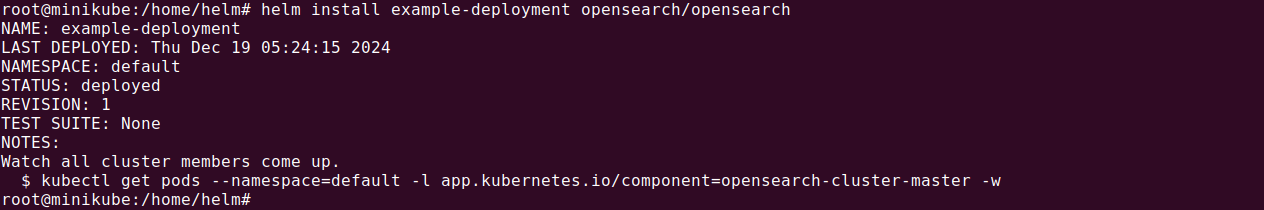
Use the following Helm command to deploy OpenSearch with the default settings:
|
1 |
helm install example-deployment opensearch/opensearch |
In this command:
example-deployment: A name for your deployment.opensearch/opensearch: Specifies the chart to install.
Step 4: Customize OpenSearch configuration
To customize the deployment, create a customvalues.yaml file where you can override default settings. For example, to set a custom admin password, define it under extraEnvs in the customvalues.yaml file:
|
1 2 3 |
extraEnvs: - name: OPENSEARCH_INITIAL_ADMIN_PASSWORD value: my-secure-password |
Deploy OpenSearch with the customized configuration:
|
1 |
helm install --values=customvalues.yaml opensearch-2.0.0.xyz |
Step 5: Verify the deployment
- Check the status of the deployed OpenSearch pods to ensure they are running:
|
1 |
kubectl get pods |
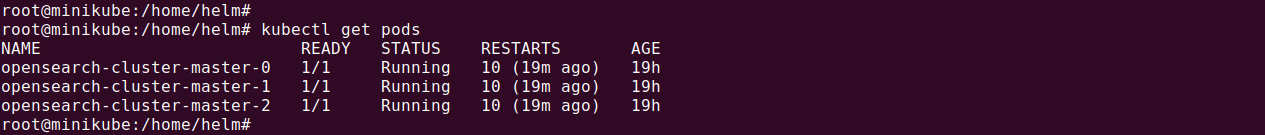
Sample output:
|
1 2 3 4 |
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE opensearch-cluster-master-0 1/1 Running 0 4m12s opensearch-cluster-master-1 1/1 Running 0 4m12s opensearch-cluster-master-2 1/1 Running 0 4m12s |
- To verify that OpenSearch is up and running, you can access the OpenSearch shell:
1kubectl exec -it opensearch-cluster-master-0 -- /bin/bash
- Send a test request to OpenSearch using curl to ensure it’s operational:
1curl -XGET https://localhost:9200 -u 'admin:my-secure-password' --insecure
The response should look similar to this:
123456789101112{"name" : "opensearch-cluster-master-1","cluster_name" : "opensearch-cluster","cluster_uuid" : "cP3gx5pPS5GLr8Z7wQm7YV","version" : {"distribution" : "opensearch","number" : "2.12.0","build_type" : "tar","lucene_version" : "8.9.0"},"tagline" : "The OpenSearch Project: https://opensearch.org/"}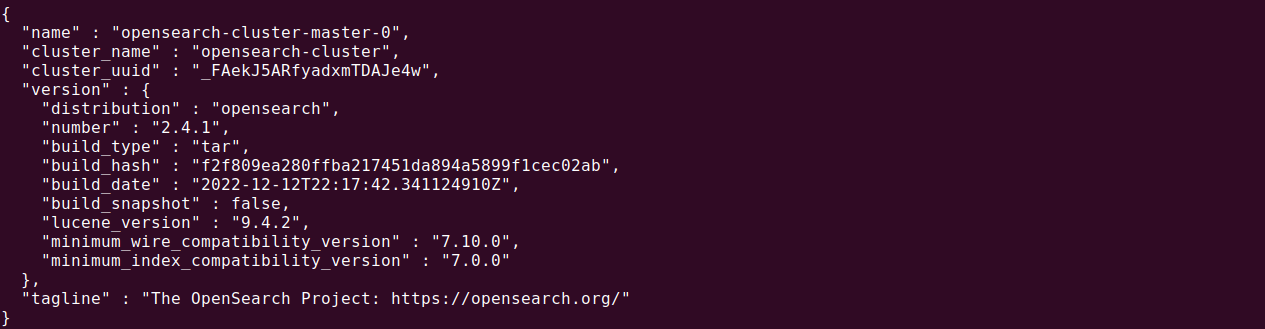
Optional: Uninstall OpenSearch
- If you need to uninstall the OpenSearch deployment, identify its name using the helm list command:
1helm list
- Sample output
12NAME NAMESPACE REVISION STATUS CHART APP VERSIONexample-deployment default 1 2024-06-17 12:00:00 +0000 UTC deployed opensearch-2.0.0 2.0.0

- Uninstall the deployment using the helm delete command:
1helm delete example-deployment
Best practices for deploying OpenSearch with Helm
Here are some important practices to keep in mind when using Helm charts to deploy OpenSearch.
Resource optimization
In OpenSearch deployments, resource optimization aids in achieving peak performance while minimizing costs. The elasticity of resource provisions via Helm charts allows for precise control over CPU and memory allocation. This offers administrators the ability to allocate resources based on empirical data, allocating reserved resources only as necessary, thus avoiding waste.
Analyzing performance metrics aids in controlling over-provisioning or under-provisioning scenarios, ensuring each pod utilizes allotted resources efficiently. Fine-tuning JVM settings in values.yaml optimizes search query handling, enhancing throughput. By continually refining these settings, organizations can ensure performance aligns with operational workloads.
Scaling OpenSearch clusters
Scaling OpenSearch clusters is necessary to handle increasing workloads or expanding datasets. Helm charts support this through adjustable parameters in the values.yaml file, allowing dynamic scaling of replicas and distribution of data nodes across the cluster. This elasticity ensures that OpenSearch maintains availability and fault tolerance as traffic increases.
Administrators should monitor cluster health and performance metrics continuously, scaling proactively before reaching thresholds that could potentially impact service quality. Proactive scaling minimizes latency during peak traffic periods and supports significant volume growth efficiently, ensuring continuous service delivery.
Monitoring and logging
Utilizing tools compatible with OpenSearch, such as Prometheus for monitoring or Kibana for log management, allows for detailed insights into system health. These tools provide real-time analytics on resource utilization, error rates, and response times, crucial for optimizing performance.
Adjusting configurations to enable structured logging captures detailed log data for troubleshooting and auditing purposes. Configuring proper log retention policies ensures that necessary logs are available for analysis while controlling storage costs.
Backup and recovery strategies
Implementing reliable backup and recovery strategies helps ensure data resilience against failures and data loss. Establishing routine, automated backups of indices using OpenSearch snapshot mechanisms or external tools is recommended. These backups should be stored securely, preferably in isolated storage solutions or cloud-based repositories.
Planning for disaster recovery involves testing restore processes regularly, ensuring backups are functional and up to date. Establishing a clear recovery plan, including defined recovery point objectives (RPO) and recovery time objectives (RTO), minimizes downtime during unforeseen events.
Securing OpenSearch deployments
Implementing encryption for data at rest and in transit is crucial, often achieved through TLS protocols, to protect sensitive information against unauthorized access. Configuring strong access control measures, such as IAM roles and permissions, limits access to critical components.
Another security measure involves deploying monitoring solutions to track unauthorized access attempts or anomalies that might indicate security breaches. Regular security audits and patch applications ensure vulnerabilities are promptly addressed, maintaining the deployment’s integrity.
OpenSearch on the Instaclustr Managed Platform: Experience the power of scalable search and analytics
Instaclustr for OpenSearch offers managed services that take the complexities of deploying and maintaining this robust platform off your plate. With expertise in open source technologies, Instaclustr ensures that your OpenSearch clusters are optimized, scalable, and always available, allowing you to focus on what truly matters: building great products and improving your customer experience.
Instaclustr for OpenSearch
When it comes to operationalizing OpenSearch, Instaclustr provides several key benefits:
1. Fully managed OpenSearch
Get end-to-end management for your OpenSearch deployment, including setup, scaling, monitoring, and routine maintenance. Stay focused on scaling your business while Instaclustr handles the grunt work of managing your platform.
2. High availability and scalability
Instaclustr ensures high availability with multi-node configurations that provide failover capabilities. Whether you’re running a small application or scaling to enterprise-grade workloads, Instaclustr helps your OpenSearch clusters grow seamlessly with your business needs.
3. Open source expertise
As a champion of open source technology, Instaclustr eliminates vendor lock-in and with the crucial benefit of transparent pricing. This commitment ensures that your OpenSearch deployment is always community-driven, independently audited, and aligned with the latest developments in the ecosystem.
4. World class support
Instaclustr’s focus on customer success means you receive 24×7 support from seasoned OpenSearch engineers. No chatbots; just real people ready to solve real problems and help you make the most of your investment.
5. Monitoring and optimization
Instaclustr doesn’t just manage your OpenSearch cluster—they actively monitor and optimize its performance. Advanced analytics and proactive alerts mean you’re always one step ahead when it comes to performance issues.
For more information see: